
Why companies use ratings for carbon credit due diligence
Third-party ratings can speed up due diligence for carbon credit buyers by offering an impartial, expert, and project-level view on credit quality.
Climate-conscious companies around the world are turning to carbon ratings to build credible carbon portfolios with defensible environmental claims.
Carbon credit retirement data shows that demand for highly-rated credits is on the rise, and that buyers are willing to pay a premium for high quality.
Contents
- Ratings provide a project-level assessment of carbon credit quality
- Buyers and sellers use ratings to identify high-quality, low-risk carbon credits
- Demand is growing for higher-rated credits and falling for lower-rated credits
- These demand trends are increasingly reflected in market prices
- What you need to remember
As the market’s most trusted ratings agency, BeZero Carbon has unique insight into how companies think about carbon credit quality.
High ratings have become a key component of credit procurement criteria. To demonstrate both the credibility of their credit holdings and the defensibility of their climate claims, major buyers across Asia, Europe, and the US are treating third-party carbon ratings as an essential reference for quality. Many buyers are now requesting a minimum rating as a specified condition of purchase, whether buying through advisors, marketplaces or through their own in-house procurement departments.
Data around buyer behaviour supports this; demand for highly-rated credits is on the rise, and this trend is reflected in credit prices. This brief explainer illustrates how companies are turning to the BeZero Carbon Rating to de-risk their credit purchases.
Ratings provide a project-level assessment of carbon credit quality
Carbon ratings assess the likelihood that a given carbon credit represents one tonne of emissions avoided or removed. Ratings put projects of all types on a level playing field by creating a simple metric by which to compare the quality of the credits these projects generate.
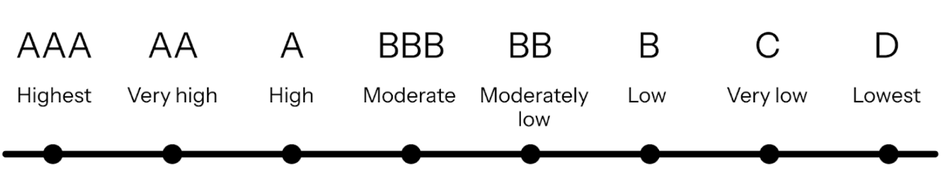
Figure 1: The BeZero Carbon Rating scale. Each letter rating represents a likelihood a carbon credit delivers on its promise of 1 tonne of CO2e avoided or removed.
BeZero Carbon Ratings are based on rigorous, project-specific assessments across the key drivers of quality, including additionality, accurate carbon accounting, and permanence. The rating process draws on detailed scientific and financial analysis and often makes use of cutting-edge technologies such as geospatial analysis and machine learning.
Buyers and sellers use ratings to identify high-quality, low-risk carbon credits
The majority of end buyers want to ensure that the carbon credits they purchase are high-quality. Research by BCG backs this up: based on a survey of almost 500 company leaders, they found that most buyers are willing to pay a premium for high-quality credits. They also found that the key attribute sought by credit buyers is demonstrable greenhouse gas impact.
However, undertaking an objective assessment of carbon project quality is challenging: it requires deep technical expertise and access to specific data sources, making it impractical for many sustainability leaders to do this in-house, particularly considering the thousands of projects with available credits on the market. This is where ratings agencies come into play: they provide much-needed information on project risks using a simple quality metric that is comparable across all types of credits.
Since carbon ratings were launched, end buyers and intermediaries have been able to use them to identify lower-risk projects for the first time and change their purchasing strategy to reflect this.
"Understanding how BeZero analyses various risk factors for determining carbon credit ratings is beneficial to understand the checkpoints for credit procurement."
- Sumitomo Corporation
Demand is growing for higher-rated credits and falling for lower-rated credits
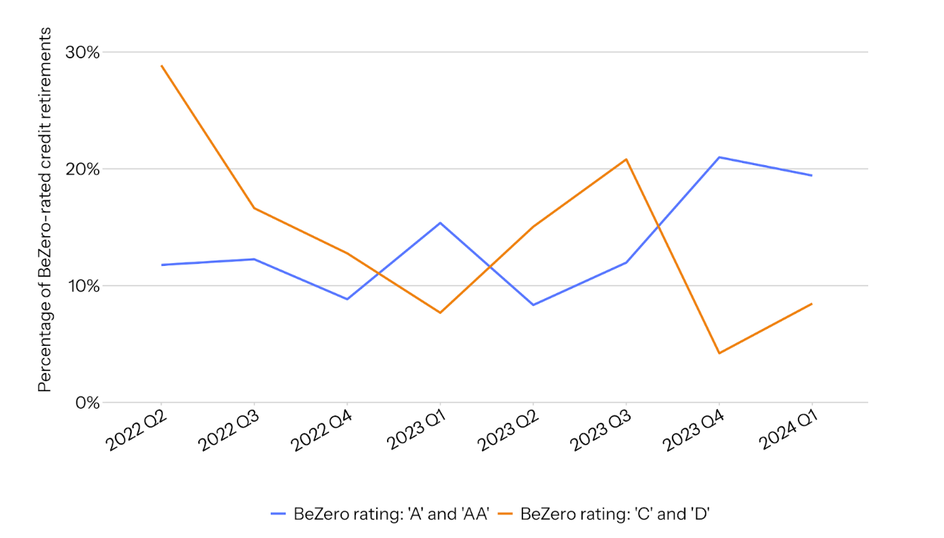
Figure 2. Percentage of retirements of BeZero-rated credits rated either ‘A’ and higher or ‘C’ and lower, for 2022 Q2 - 2024 Q1.¹
Anecdotal evidence regarding buyer preference for high-quality credits and use of ratings to guide purchasing decisions is increasingly backed up by quantitative market data. Retirements data from the voluntary carbon market indicates that buyers are showing a growing preference for higher-rated credits over lower-rated credits. Figure 2 shows that over the last two years, the percentage of BeZero-rated retirements with a rating of ‘C’ or ‘D’ (the lowest levels on our rating scale) has fallen from around 30% to under 10%, while the percentage of BeZero-rated retirements with a rating of ‘A’ or ‘AA’ (the highest ratings that have been assigned so far) has risen from around 10% to around 20%.
"Buyers are asking for conditions in long-term offtake agreements, that if a BeZero Carbon Rating drops below BBB, they have the ability to back out of the commitment."
- US-based carbon marketplace
These demand trends are increasingly reflected in market prices
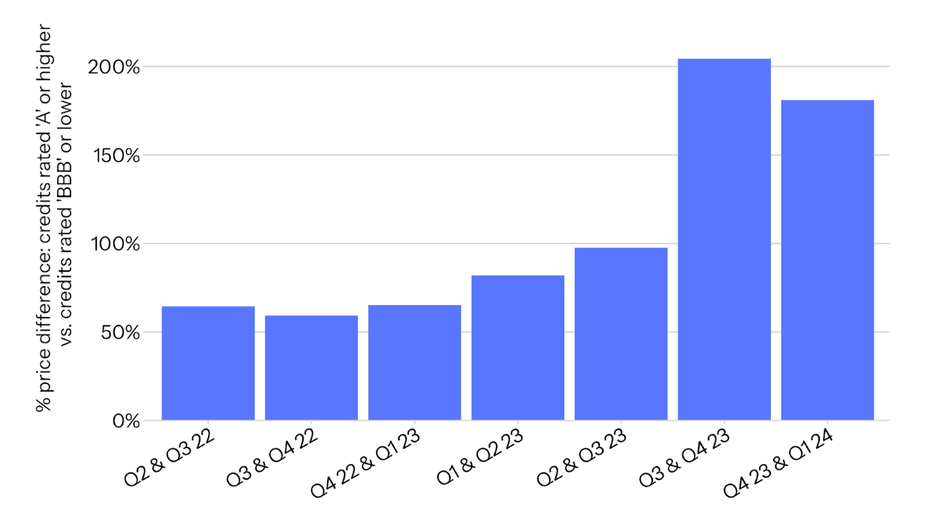
Figure 3. The average percentage price difference between credits with a BeZero rating of ‘A’ or higher vs. credits with a BeZero rating of ‘BBB’ or lower for six-month periods from Q2 2022-Q1 2024. Pricing data from Xpansiv’s CBL exchange.
There is also evidence of a growing buyer preference for higher-rated credits within pricing data. Figure 3 shows that over the last two years, there has been a steady increase in the percent price difference between credits with a BeZero Carbon Rating of ‘A’ or higher compared to those rated ‘BBB’ or lower. The price premium for higher-rated credits has risen substantially over the last nine months in particular, reaching around 200%.
When retiring credits, companies can use carbon ratings to make credible green claims
Companies buy carbon credits for the purpose of retiring them, thereby delivering on the credits’ climate impact potential of credits and enabling the company to make green claims. Recently, many governments have taken legislative action to ensure the transparency of any green claims made using carbon credits, such as by requiring the disclosure of key attributes of the relevant carbon credits. Examples include the EU’s Green Claims Directive and Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive, and California’s AB 1305 law.
Corporates can make their green claims even more credible by including carbon ratings as part of the information they disclose to substantiate those claims. Ratings provide an easily understandable metric which provides an independent expert opinion on the quality of carbon credits used to make claims.
Beyond simply disclosing the ratings of retired credits, corporates may wish to go further by using ratings to ‘risk-adjust’ their claims. The principle of this approach is to discount the assumed emissions impact of a given credit by a factor linked to its rating, with lower-rated credits discounted to a greater degree. By discounting in this way, any green claims are more likely to reflect the true climate impact of a portfolio of retired credits.
You can learn how this approach works in practice in this illustrative example, or by reading BeZero’s white paper, Making Credible Claims, from which we drew the discount factors in Table 1 below.
Table 1. Proposed discount factors for each BeZero Carbon Rating notch.²
| BeZero Carbon Rating | AAA | AA | A | BBB | BB | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discount factor on 1t per credit | 5% | 10% | 20% | 30% | 50% | 70% | 90% | 99% |
What you need to remember
There is a growing link between carbon credit quality and price, with buyers better equipped than ever to build a portfolio that will deliver climate action.
Because BeZero’s headline ratings are public, any credit buyer can check project quality for themselves. Companies can independently verify what their advisors are recommending, what a developer is claiming, or how a broker is pricing a credit.
As a universal reference point, carbon ratings help to remove doubt. Sustainability leaders around the world can use ratings for assurance that the carbon credits used in their climate strategy have credible impact, and that their associated green claims are defensible.
By signing up for BeZero’s public ratings, you also gain access to market trends and project screening tools - register here to explore project listings, headline ratings, and hundreds of articles on all things carbon. Paying subscribers to BeZero’s platform can dig deeper into the analysis behind each rating, and benefit from a comprehensive suite of portfolio analytics, risk assessment and geospatial monitoring tools.
In the next article in our carbon credit explainer series, you’ll learn what it takes to rate a carbon project, from the cutting-edge techniques employed to the cross-disciplinary expertise needed. Read more here.
References
Covers retirements of credits accredited by Verra, Gold Standard, American Carbon Registry, Climate Action Reserve, Puro.Earth, and Cercarbono.
Note these discount factors are derived using a combination of data available through the BeZero Carbon Rating and our analytical view on the appropriate discount factor to attach to the qualitative element of the assessment underlying the BeZero Carbon Rating.